Description
MTP® trunk cable is designed to provide high-density connections between network equipment in data centers which need space savings and reduced cable management troubles. With US Conec MTP® connectors and Corning MIC® 250 2.0 Cable, it is optimized for fiber optics direct connection and high-density data center applications such as high-bandwidth routers and high-density data clusters, and uses a simple push/pull latching mechanism for easy insertion and removal.
Specifications:
- Made in the USA (Palmer, MA)
- Connectors A & B: MTP® Male
- Fiber Type: OM4 (multi-mode 50/125μm)
- Wavelengths: 850nm / 1300nm
- Fiber Brand: Corning MIC® 250 2.0 Cable
- Fiber Count: 12
- Polish Type: UPC
- Jacket OD: 5.5mm
- Jacket color: Aqua
- Cable Rating: OFNP (Plenum)
- Polarity: Type B
- Minimum Bend Radius: 27.5mm
- RoHS Compliant: Yes
Urgent order? Please contact: CustomerService@americancableassemblies.com
MPT®/MPO CONNECTOR POLARITY
Each MPT®/MPO connector has a key on one side of the connector body. The “Key Up” position refers to the orientation where the key is located at the top position of the connector. When looking at the end face of the connector, position 1 is on the far left while position 12 is on the far right. Depending on the adopted connectivity orientation, the MPO adapter needs to be suitable for its application, which is either “Key Up to Key Down” or “Key Up to Key Up”.
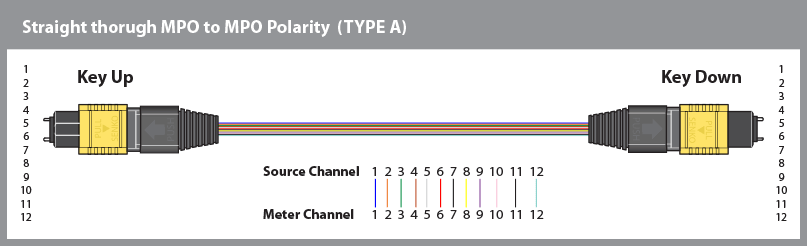
Method A:
Patch Cord Polarity Flip
The Patch Cord Polarity Flip, also known as the Transmit-Receive Flip, has fiber 1 in position 1 in the MPO connector at both ends of the patch cord and is maintained throughout the network. This method is the simplest design to install and maintain, as the orientation of the connector remains consistent.
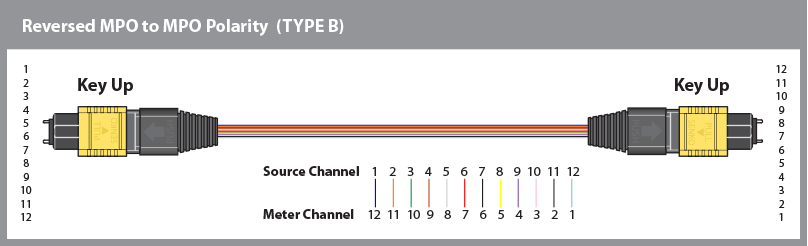
Method B:
Adapter Polarity Flip
As stated in the name Adapter Polarity Flip, the polarity at one end of the connector is flipped. At one end of the connector fiber 1 is located at position 12 while fiber 12 is located at position 1. The connector orientation at the Transceiver and Receiver end are the same.